What is Excavation? and what machines should you use?
Excavation is described as a method of digging or hollowing out a particular area of ground. However, the term is loosely used across several working sectors to describe a particular process of work. During this resource, we are going to explain a bit more about excavation and how it applies to the construction industry.
Construction excavation has always existed, as far back as we can imagine. There is plenty of evidence around the world to prove that the process of excavation has been around forever.
But in this day and age, why do we need to excavate?
Why Do We Excavate?
Excavating is far much more than just digging a hole in the ground. There is far more purpose in the methods of excavation. This could be to prepare the land, install proper drainage, trenching or even remove on contaminated earth.
The specific reason why we excavate totally depends on the requirements of our project. Excavation is can assist in several jobs that require digging, including landscaping, road building, and much more. The type or size of equipment that you use is suitable to your project’s requirements depending on their goals. This includes using different excavation methods to achieve your desired outcome.
Let’s look at the different types of excavation to see how different methods suit various applications.

The Types Of Excavation
Stripping
Also known as the ‘cut and fill’ method of excavation. This type of excavation practice is can cover a huge area but at very shallow intervals. Excavation like this is popular in landscaping, highway, and rail construction. Stripping includes the removal of topsoil and rock from the site. It is a long process but is one of the most delicate excavation practices.
Trenching
Trenching is very different. This method consists of excavating holes that are longer than they are wide. This process allows you to install utilities under the ground without having to remove the entire area. This method is very popular in the early phases of construction projects. However, it can be the favoured method when working in small confined spaces.
Basement
Basement excavation refers to when a project requires digging an underground level of a building. Essentially digging an underground room and foundations to build upward on. Basements are not as popular as they used to be, however, this type of excavation method is still used in several daily practices.
Dredging
The process of dredging is very different from the previous methods we have covered. Dredging is the process of removing sediments and other materials from underwater. This is done from a raft, barge, or by special equipment from the waterside. The dredging process aims to remove unwanted materials, reshape waterbeds and encourage better drainage overall.
Borrow Excavation
Borrow excavation describes the borrowing of materials, such as earth, gravel, sand, etc. to use on another location on a building site. The process of handling these types of materials, we call barrow excavation. This normally takes place with imported materials. Materials like these can be used to backfill, grade, or mix with other materials to form construction compounds. E.g.: Concrete.
Drainage Excavation
Drainage excavation, in most cases, is to expose damaged drains, piping or utilities that are under the ground. The method of exposure is conducted by digging small trenches deep enough, only where necessary. This allows engineers to directly access the existing drains so that repairs or maintenance can take place safely.
Are There Laws on Excavation?

There is currently no legislation as to what depth you can excavate on private land in the UK. However, there are specific regulations that must be adhered to. Excavations over a depth of 5ft (1.5m) must install appropriate safety cave-in protection systems.
Some examples of methods that can you can adopt:
- Sloping
- Benching
When excavating more than 20ft in depth, the slope or benching must be designed by a registered professional engineer. For more information on correct practices, visit the HSE website here.
What Is “Sloping” When Excavating?
Sloping is an excavation technique that is conducted when the basin depth exceeds 5ft. This is a safety method to protect employees from cave-ins. The sloping incline becomes shallower depending on the type of soil and depth you require to reach.
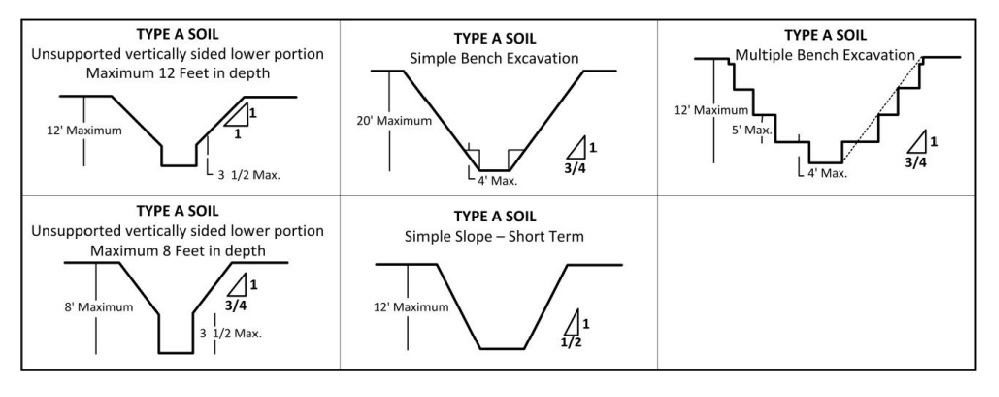
What Is “Benching” When Excavating?
Benching is an alternative method to sloping, which is designed to protect employees from cave in during excavation. Benching consists of incremental steps, which are horizontal or gently slopped, depending on the depth and soil type.
There are two different types of benching, simple and multiple. As a general rule, the bottom vertical height of the trench must not exceed 4ft from the first bench.
The Effects Of Soil Type On Sloping And Benching
The largest deciding factor contributing to which method of protecting employees from cave-ins is the soil type. Soil types are determined before excavation takes place, and are very important to the safety of large projects. Determining what soil classification you are excavating allows you to choose the correct method of cave-in protection.
There are 4 types of soil classification:
- Stable Rock is defined as a solid mineral.
- Type A soils are defined as cohesive soils with an unconfined compressive strength of 1.5 tons per square foot (sf) or greater (i.e. clay, silty clay, sandy clay, clay loam and cemented soils)
- Type B soils are defined as cohesive soil with an unconfined compressive strength of 0.5 psf or greater but less than 1.5 tsp (i.e. angular gravel, silt, silt loam, and sandy loam)
- Type C soils are defined as soils with an unconfined compressive strength of 0.5 psf or less (i.e. gravel, sand, and loamy sand)
How Soil Classification Affects Sloping Excavation
When using a sloping method of excavation over a depth of 5ft, the following method procedures should be followed:
| Soil Class | Height | Depth Ratio | Slope Angle |
| Stable Rock | Vertical | N/a | 90 |
| Type A Soil | Max allowable slope | 3/4:1 | 53 |
| Type B Soil | Max allowable slope | 1:1 | 45 |
| Type C Soil | Max allowable slope | 1 1/2:1 | 34 |
The more stable the soil type, the steeper the angle of excavation can be. Remember that if excavation is to surpass 20ft, a registered professional must construct the deisgn.
How soil classification affects benching excavation
Benching can only take place in soil classifications ‘stable rock, type A and type B. This method is not safe to use for extremely sandy soils that have a higher probability of moving during construction. The bottom of a benching trench can be vertical to a depth of 5ft in type A soil and 4ft in type B soil to a total trench depth of 20ft.
Machinery Used In Excavation
Since we have discovered a lot about excavating already, it is time to uncover what types of machinery we can use for an excavation project. There are many pieces of equipment on the market that can assist, some more specialised than others. Let’s take a look…
Backhoe loader
The backhoe loader is a classic piece of excavation equipment. The machine consists of a loading bucket on the front of the machine and an excavating arm and bucket on the rear. These machines are useful for a number of tasks throughout the construction industry. It is important to note that these multipurpose machines can operate on several terrains and are very versatile.
Unlike other equipment, Backhoes are the preferred option for tasks such as snow removal, farming, loading, and medium-sized construction and excavation projects.
Skid Steer loader
A Skid steer loader is a small, rigid framed machine that has two lifting arms attached to its front. These small excavating machines off a scooping action that can be used to move materials and earth. These machines are commonly found in the landscaping and development sectors. Their size a simplicity makes them ideal for less experienced operators working in small, confined areas.
Excavator
Probably the most renowned piece of machinery designed for digging holes. The excavator provides heavy lifting and 360-degree rotation. This machine consists of a large arm with an attached bucket and a cabin on tracks or wheels.
Excavators are used for a wide range of projects, such as demolition, digging trenches, snow removal, grading the ground, etc. There are multiple different variations of excavators on the market to choose from depending on your project requirements. Excavators are commonly chosen when a huge number of debris or materials needs to be moved.
Where To Hire Excavating Equipment From In The UK?

WHC Hire Services operates one of the most efficient fleets of high-performance excavation equipment in the UK. With a huge range of low-hours equipment brought to you by some of the world’s finest manufacturers, WHC has a solution for every type of excavation project. WHC offers excavators ranging from Micro- 28T.
With regular investment into the quality of our fleet, we can help equip customers and businesses with right equipment to get the job done. For more information on Excavators to hire, see our online catalogue, or call 01684377977 today.

